‘A To Z Computer Full Form’ PDF Quick download link is given at the bottom of this article. You can see the PDF demo, size of the PDF, page numbers, and direct download Free PDF of ‘Full Form In Computer’ using the download button.
Computer Related Sparts Full Form List PDF Free Download
Computer All Short Form With Full Form
1GL – First-Generation Programming Language
2GL – Second-Generation Programming Language
3GL – Third-Generation Programming Language
4GL- Fourth Generation Programming Language
5GL -Fifth Generation Programming Language
286 – Intel 80286 processor
386 – Intel 80386 processor
486 – Intel 80486 processor
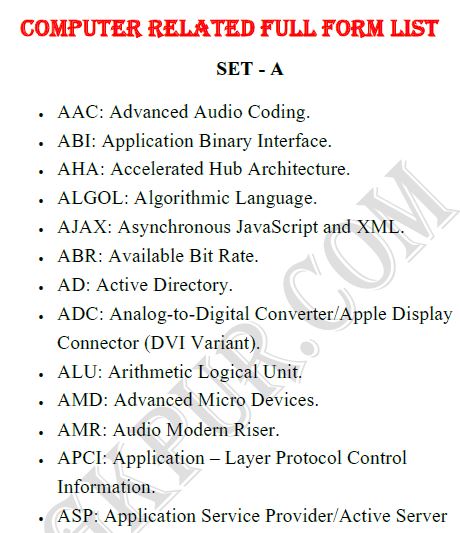
SET – A
ADC: Analog – to – Digital Converter / Apple Display Connector (DVI Variant).
ALU: Arithmetic Logical Unit.
AMD: Advanced Micro Devices.
AAC: Advanced Audio Coding.
ABI: Application Binary Interface.
AHA: Accelerated Hub Architecture.
AD: Active Directory.
ATA: Advanced Technology Attachment.
API: Application Programming Interface.
AVC: Advanced Video Coding.
AVI: Audio-Video Interleaved.
ALGOL: Algorithmic Language.
AJAX: Asynchronous JavaScript and XML.
ABR: Available Bit Rate.
AWT: Abstract Window ToolKit.
ARPANET: Advanced Research Projects Agency Network.
ASCII: American Standard Code for Information Interchange.
ATM: Asynchronous Transfer Mode.
AMR: Audio Modern Riser.
APCI: Application – Layer Protocol Control Information.
ASP: Application Service Provider / Active Server Pages.
AST: Abstract Syntax Tree.
SET – B
BASIC: Beginner All-Purpose Symbolic Instruction Code.
BAL: Basic Assembly Language.
BER: Bit Error Rate.
BFD: Binary File Descriptor.
BGP: Border Gateway Protocol.
BiDi: Bi-Directional.
BIN: Binary.
BW: Bandwidth.
BIT: A Binary Digit.
BLOB: Binary Large Object.
BLOG: Web Log.
BINAC: Binary Automatic Computer.
BCD: Binary Coded Decimal.
BMP: Basic Multilingual Plane.
BT: BitTorrent/Bluetooth.
BIOS: Basic Input Output System.
BPS: Bits Per Second.
SET – C
CSI: Common System Interface.
CSV: Comma–Separated Values.
CTCP: Client–to–Client Protocol.
CAI: Computer-Aided Instruction.
CAQA: Computer-Aided Quality Assurance.
CC: C Compiler/Carbon Copy.
CAD: Computer-Aided Design.
CGA: Color Graphics Array.
CD-R: Compact Disk–Recordable.
CD-ROM: Compact Disk–Read-Only Memory.
CTS: Clear to Send.
CUA: Common User Access.
CNC: Computer Numerical Control.
COBOL: Common Business–Oriented Language.
CAE: Computer-Aided Engineering.
CD: Compact Disk/Change Directory.
CDMA: Code Division Multiple Access.
CD-RW: Compact Disk – Rewritable.
CG: Computer Graphics.
CIFS: Common Internet File System.
CIM: Common Information Model.
CGI: Common Gateway Interface/Computer–Generated Imaginary.
CMOS: Complementary Metal – Oxide Semiconductor.
CLI: Command Line Interface.
CRS: Computer Reservation System.
CTR: Cathode Ray Tube.
CTL: Computation Tree Logic.
CPU: Central Processing Unit.
SET – D
DAP: Direct Access Protocol.
DFS: Distributed File System.
DBA: Database Administrator.
DAT: Digital Audio Tape.
DB: DataBase.
DOS: Disk Operating System.
DPI: Dots per INCH.
DVD: Digital Versatile Disk/Digital Video Disk.
DMA: Direct Memory Access.
DOS-PMI: Disk Operating System – Protected Mode Interface.
DLL: Dynamic Link Library.
DLP: Digital Light Processing.
DCC: Direct Client–to–Client.
DDR: Double Data Rate.
DES: Data Encryption Standard.
DFD: Data Flow Diagram.
DAO: Data Access Objects.
DBMS: Database Management System.
DHTML: Dynamic Hyper Text Markup Language.
DIVX: Digital Video Express.
DVE: Digital Video Effects.
DNS: Domain Name System.
DVR: Digital Video Recorder.
DVD-R: Digital Versatile Disk – Recordable.
DBSN: Database Source Name (ODBC).
DTE: Data Terminal Equipment.
DTR: Data Terminal Ready.
DSL: Digital Subscriber Line/Domain–Specific Language.
DVD-RW: Digital Versatile Disk–Rewritable.
DVI: Digital Visual Interface.
DVD-ROM: Digital Versatile Disk – Read-Only Memory.
SET – E
EOM: End of Message.
EPROM: Erasable Programmable Read-Only Memory.
EID: Electronic ID Card.
ECU: Extended Unix Code.
EEPROM: Electronically Erasable Programmable Read-Only memory.
ENIAC: Electronic Numerical Integrator and Computer.
EOF: End of File.
EOL: End of Line.
EST: Electrostatic Discharge.
EXE: Executable.
EBCDIC: Extended Binary Coded Decimal Interchange Code.
EIGRP: Enhanced Interior Gateway Routing Protocol.
ELF: Executable and Linkable Format.
ELM: Electronic Mail.
SET – F
FS: File System.
FCS: Frame Check Sequence.
FPU: Floating Point Unit.
FDD: Floppy Disk Drive.
FDMA: Frequency-Division Multiple Access.
FIFO: First In First Out.
FSB: Front Side Bus.
FTP: File Transfer Protocol.
FXP: File Exchange Protocol.
FHS: Filesystem Hierarchy Standard.
FAT: File Allocation Table.
FAQ: Frequently Asked Questions.
FDC: Floppy Disk Controller.
SET – G
GIGO: Garbage In Garbage Out.
GPL: General Public License.
GCR: Group Code Recording.
GPU: Graphics Processing Unit.
GUI: Graphical User Interface.
GB: Gigabyte.
GDI: Graphics Device Interface.
GIF: Graphics Interchange Format.
Gb: Gigabit.
GPRS: General Packet Radio Service.
SET – H
HAL: Hardware Abstraction Layer.
HTX: Hyper Transport Expansion.
HURD: Hird of Unix-Replacing Daemons.
HVD: Holographic Versatile Disk.
HZ: Hertz.
HTM: Hierarchical Temporal Memory.
HTML: Hypertext Markup Language.
HCI: Human-Computer Interaction.
HID: Human Interface Device.
HIG: Human Interface Guidelines.
HP: Hewlett-Packard.
HD DVD: High Definition DVD.
HDL: Hardware Description Language.
HHD: Hybrid Hard Drive.
HTTP: Hypertext Transfer Protocol.
HTTPD: Hypertext Transfer Protocol Daemon.
HPFS: High-Performance File System.
HT: Hyper-Threading.
HD: High Density.
HDD: Hard Disk Drive.
SET – I
IP: Internet Protocol.
IPX: Internetwork Packet Exchange.
IRC: Internet Relay Chat.
ICP: Internet Cache Protocol.
IDE: Integrated Development Environment/Integrated Drive Electronics.
IE: Internet Explorer.
IGMP: Internet Group Management Protocol.
IMAP: Internet Message Access Protocol.
I/O: Input/Output.
ICT: Information and Communication Technology.
IDL: Interface Definition Language.
ISO: International Organisation for Standardization.
IT: Information Technology.
IBM: International Business Machines.
IC: Integrated Circuit.
ICMP: Internet Control Message Protocol.
IHV: Independent Hardware Vendor.
IGRP: Interior Gateway Routing Protocol.
IM: Instant Messaging.
IPC: Inter-Process Communication.
IPP: Internet Printing Protocol.
IPsec: Internet Protocol Security.
IPTV: Internet Protocol Television.
IIOP: Internet Iner-Orb-Protocol.
IIS: Internet Information Server.
ITU: International Telecommunication Union.
ISOC: Internet Society.
ISP: Internet Service Provider.
ISR: Interrupt Service Routine.
ISV: Independent Software Vendor.
IrDA: Infrared Data Association.
IRP: I/O Request Packet.
IRQ: Interrupt Request.
ISC: Internet Storm Center.
SET – J
J2EE: Java 2 Enterprise Edition.
J2ME: Java 2 Micro Edition.
J2SE: Java 2 Standard Edition.
JSP: Java Server Pages.
JDK: Java Development KIT.
JUG: Java User Group.
JPEG: Joint Photographic Experts Group.
JRE: Java Runtime Environment.
JS: JavaScript.
JSON: JavaScript Object Notation.
SET – K
Kb: Kilobit.
KBPS: Kilobit per second.
KHz: Kilohertz.
KB: Kilobyte.
KVM: Keyboard, Video, Mouse.
SET – L
LAN: Local Area Network.
LED: Light-Emitting Diode.
LIFO: Last In First Out.
LSB: Least Significant Bit.
SET – M
MBR: Master Boot Record.
MIDI: Musical Instrument Digital Interface.
MMU: Memory Management Unit.
MMX: Multi-Media Extensions.
MHz: Megahertz.
MPEG: Motion Pictures (coding) Experts Group.
MVS: Multiple Vendor System.
MPL: Mozilla Public License.
MBCS: Multi Byte Character Set.
MDI: Multiple Document Interface.
MICR: Magnetic Ink Character Recognition.
MAN: Metropolitan Area Network.
MANET: Mobile Ad-Hoc Network.
Mb: Megabit.
MB: Megabyte.
MSB: Most Significant Bit.
MNG: Multiple-image Network Graphics.
MOSFET: Metal-Oxide-Semiconductor Field-Effect Transistor.
MIMO: Multiple-Input Multiple Output.
MIPS: Million Instructions Per Second.
MIME: Multipurpose Internet Mail Extensions.
MS-DOS: Microsoft Disk Operating System.
SET – N
NIC: Network Interface Controller.
NIO: New I/O.
NMI: Non-Maskable Interrupt.
NNTP: Network News Transfer Protocol.
NTP: Network Time Protocol.
NOP: NO Operation.
NOS: Network Operating System.
NT (Windows): New Technology.
NTFS: NT File System.
NFS: Network File System.
NVRAM: Non-Volatile Random Access Memory.
SET – O
OCR: Optical Character Reader.
OOP: Object-Oriented Programming.
OS: Operating System.
OSS: Open Source Software.
OPML: Outline Processor Markup Language.
SET – P
PATA: Parallel ATA.
PC DOS: Personal Computer Disk Operating System.
P2P: Peer-To-Peer.
PPC: Power PC.
PPI: Pixels Per Inch.
PLC: Power Line Communication / Programmable Logic Controller.
Pnp: Plug-and-Play.
PGA: Pin Grid Array.
PC: Personal Computer.
PCB: Printed Circuit Board.
PPP: Point-to-Point Protocol.
PPPoA: PPP over ATM.
PPPoE: PPP over Ethernet.
PPTP: Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol.
PAN: Personal Area Network.
PAP: Password Authentication Protocol.
PCI: Peripheral Component Interconnect.
PCIe: PCI Express.
PCL: Printer Command Language.
PERL: Practical Extraction and Reporting Language.
PIO: Programmed Input/Output.
PSU: Power Supply Unit.
PHP: PHP: Hypertext Preprocessor.
PIC: Peripheral Interface Controller / Programmable Interrupt Controller.
PINE: Program for Internet News & Email.
PoE: Power Over Ethernet.
POST: Power-On Self Test.
SET – Q
QDR: Quad Data Rate.
QFP: Quad Flat Package.
QFP: Quick File Access.
QoS: Quality of Service.
SET – R
RF: Radio Frequency.
RGB: Red, Green, Blue (RGBA- Red, Green, Blue, Alpha).
RDF: Resource Description Framework.
RAIT: Redundant Array of Inexpensive Tapes.
RAM: Random Access Memory.
RARP: Reverse Address Resolution Protocol.
REEAL: Recursive Functions Algorithmic Language.
RTOS: Real-Time Operating System.
RIP: Routing Information Protocol.
ROM: Read-Only Memory.
ROMB: Read-Out Motherboard.
RAD: Rapid Application Development.
RADIUS: Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service.
RAID: Redundant Array of Independent Disks.
RDBMS: Relation Database Management System.
ROM-DOS: Read Only Memory-Disk Operating System.
SET – S
SAN: Storage Area Network.
SATA: Serial ATA.
SAX: Simple API of XML.
SBP-2: Serial Bus Protocol 2.
SBU: Standard Build Unit.
SVGA: Super Video Graphics Array.
SFTP: Secure FTP/Simple File Transfer Protocol.
SDL: Simple Direct Media Layer.
SDN: Service Delivery Network.
SDR: Software-Defined Radio.
SMBIOS: System Management BIOS.
SMTP: Simple Mail Transfer Protocol.
SP: Service Pack.
SHDSL: Single-pair High-speed Digital Subscriber Line.
SPI: Serial Peripheral Interface.
SQL: Structured Query Language.
SCSI: Small Computer System Interface.
SDRAM: Synchronous Dynamic Random Access Memory.
SUS: Single UNIX Specification.
SVD: Structured VLSI Design.
SVG: Scalable Vector Graphics.
SIMD: Single Instruction, Multiple Data.
SIMM: Single Inline Memory Module.
SET – T
TB: TeraByte.
TCP: Transmission Control Protocol.
TCP/IP: Transmission Control Protocol / Internet Protocol.
TDMA: Time Division Multiple Access.
TTF: True Type Font.
TTL: Transistor-Transistor-Logic.
TMP: Temporary.
TTA: True Tap Audio.
TTS: Text-to-Speech.
TTY: Teletype.
SET – U
UEFI: Unified Extensible Firmware Interface.
UI: User Interface.
UPS: Uninterruptible Power Supply.
URN: Uniform Resource Name.
USB: Universal Serial Bus.
UTF: Unicode Transformation Format.
URI: Uniform Resource Identifier.
UTP: Unshielded Twisted Pair.
UL: Upload.
URL: Uniform Resource Locator.
UAC: User Account Control.
UART: Universal Asynchronous Receiver Transmitter.
SET – V
VAR: Variable.
VB: Visual Basic.
VBA: Visual Basic for Applications.
VBS: Visual Basic Script.
VFAT: Virtual FAT.
VFS: Virtual File System.
VGA: Video Graphics Array.
VT: Video Terminal.
VLAN: Virtual Local Area Network.
VM: Virtual Memory.
VOD: Video On Demand.
VoIP: Voice Over IP.
VPN: Virtual Private Network.
VPU: Visual Processing Unit.
VGCT: Video Graphics Character Table.
SET – W
WAN: Wide Area Network.
WAP: Wireless Access Protocol.
WWAN: Wireless Wide Area Network.
WWID: World Wide Identifier.
WWW: World Wide Web.
WOL: Wake-on-Lan.
Wi-Fi: Wireless Fidelity.
WinFS: Windows Future Storage.
WSDL: Web Services Description Language.
WINS: Windows Internet Naming Service.
WLAN: Wireless Local Area Network.
WMA: Windows Media Audio.
WMV: Windows Media Video.
WUSB: Wireless Universal Serial Bus.
WOM: Wake-on-Modem.
WPA: Wi-Fi Protected Access.
SET – X
XAML: Extensible Application Markup Language.
XHTML: Extensible Hypertext Markup Language.
XSLIT: Extensible StyleSheet Language Transformations.
XSL: Extensible Stylesheet Language.
XSL-FO: Extensible StyleSheet Language Formatting Objects.
XUL: XML User Interface Language.
XMMS: X MultiMedia System.
XML: Extensible Markup Language.
XNS: Xerox Network Services.
SET – Z
ZISC: Zero Instruction Set Computer.
ZIFS: Zero Insertion Force Socket.
ZMA: Zone Multicast Address.
Sample Questions Related To Computer Abbreviations
For the reference of candidates, given below are the sample questions based on computer abbreviations.
Q 1. What does “U” stand for in “URL”?
- Uniform
- United
- Unicode
- Universal
- Unit
Answer: (1) Uniform
Q 2. What does COBOL stand for?
- Common Business Organised Language
- Common Business Oriented Language
- Code for Business Oriented Langauge
- Code of Business Organised Language
- Computer Basic Language
Answer: (2) Common Business Oriented Language
Q 3. What is the full form of WiFi?
- Wireless Fidelity
- Wireless Internet Federation
- Wireless Internet
- Wireless Internet Facility
- None of the Above
Answer: (1) Wireless Fidelity
Q 4. What does “L” stand for in “XML”?
- Link
- Language
- Loading
- Linux
- Laser
Answer: (2) Language
Q 5. What does PNG stand for?
- Portable Graphics
- Processed Network Graphics
- Personal Network Graphics
- Picture Network Graphic
- None of the Above
Answer: (3) Personal Network Graphics
| Author | – |
| Language | English |
| No. of Pages | 10 |
| PDF Size | 1 MB |
| Category | Computer |
Computer Full Form List PDF Free Download
