‘Weather, Climate, And Adaptations Of Animals To Climate Class 7 Science Notes Chapter 7 ‘ PDF Quick download link is given at the bottom of this article. You can see the PDF demo, size of the PDF, page numbers, and direct download Free PDF of ‘Weather, Climate, And Adaptations Of Animals To Climate Class 7 Science Notes Chapter 7 ‘ using the download button.
Weather, Climate, And Adaptations Of Animals To Climate Class 7 Science Notes Chapter 7 PDF Free Download
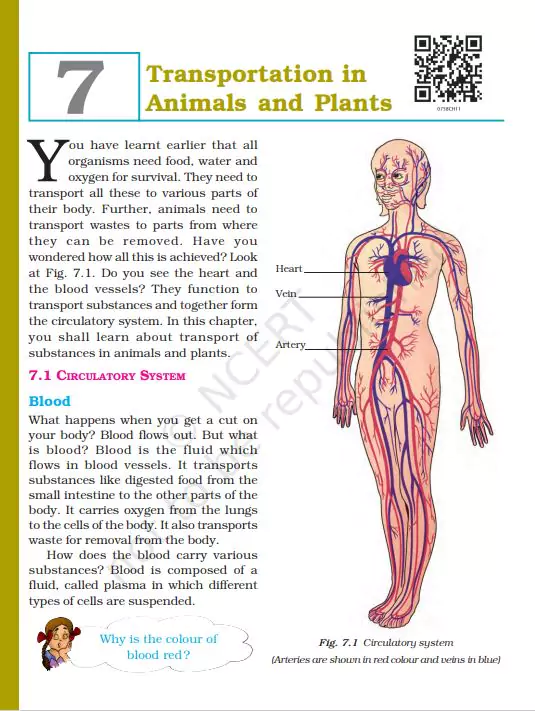
Weather, Climate, And Adaptations Of Animals To Climate Class 7 Science Notes Chapter 7
Fronts and Weather Conditions
Weather is produced by the interaction of several factors that, include:
- temperature or heat
- humidity or amount of water vapor in the air
- wind and atmospheric pressure.
- precipitation or the amount of rain
- cloudiness or the amount of cloud cover
- visibility that is how far you can look into the horizon
- Wind and an atmospheric pressure
A weather front is a boundary separating two masses of air of different densities.
- The air masses separated by a front usually differ in temperature and humidity.
- The weather analysis usually includes information about the weather fronts also.
Climate
- The average pattern of the weather recorded over a long time, say 25 years, is known as the climate of the place.
- If the temperature at a place is high mostly, then we affirm that the climate of that place is hot.
- If, on most days, there is heavy rainfall in the same place, then we affirm that the climate of that place is wet and hot.
Factors Affecting Climate
- Different factors affect climates, such as altitude, latitude, geography, and topography.
Weather vs Climate
- Meteorologists record the weather every day.
- The records of the weather have been preserved for the past several decades.
- These help us to determine the weather pattern at a place.
- The average of the weather pattern over a time period is determined by the climate.
| Basis | Climate | Weather |
| Definition | The average condition expected at a particular place in a given timeframe | The atmospheric condition at a particular point in time |
| Projection | carried out using the sum total of weather statistics over a time frame of 30 years | Periodic measurements of atmospheric pressure, rainfall, speed and direction of the wind, humidity overcasts, and other unstable factors |
| Underlying Factors | The total weather statistics for the time frame of 30 years | comprises elements like humidity, rainfall, sunlight, wind speed, a natural phenomenon like fog, frost, and so on in a particular time period |
| Study-subject | Climatology | Meteorology |
| Ingredients | comprises weather elements such as overcasts, rainfall, floods, hailstorms, winds, heatwaves, snowfall, and many more | comprises weather elements such as overcasts, rainfall, floods, hailstorms, winds, heatwaves, snowfall and many more |
| Time frame | Estimated over a longer time span | Estimated over a shorter time span |
Meteorology and Climatology
- The major focus in meteorology is weather forecasting.
- The daily weather reports are prepared by the Meteorological Department of the Government.
- This department collects data on temperature, wind, etc., and makes the weather prediction.
- Climatology is the study of climate, defined as weather conditions averaged over a period of time.
Formation and Types of Clouds
- Clouds form occurs via a phenomenon known as convection.
- As sun rays heat the ground and the immediate air over it, the warm air tends to become lighter, which is carried away along with the warm air upwards. As the air rises higher, the temperature falls, causing the amount of water vapor that the air can hold to decrease.
- This vapor condenses rapidly, and soon clouds — made up of billions of minuscule water droplets or ice crystals — result.
- Air that blows over mountains or hills is expelled upwards, leading to the development of clouds. Precipitation and clouds are often found on the windward side of a mountain.
1. Temperature
The weather is mainly affected by the sun which produces heat and raises the temperature. The sun provides light as well as heat to the earth. It is necessary for the production of energy. The < heat from the sun is absorbed by the earth’s surface, oceans, and atmosphere which plays an important role in determining the weather of any place.
Therefore, it is clear that change in weather is caused due to the sun because the changes occurring in the sun’s heat will change the atmosphere more frequently. The time of sunrise and sunset also changes throughout the year.
2. Rainfall
The amount of water droplets that fall back on the earth after condensation of water vapors is called rainfall. When the temperature is too low, these droplets in the cloud get frozen into crystals of ice and come to the earth as snowfall. During winters, the temperature falls after sunset causing condensation of water vapors near the ground. These droplets hang in the air to form fog.
Note: Rainfall is generally measured in millimeters. The instrument that is used to measure the rainfall is called a rain gauge. It is a measuring cylinder with a funnel kept on its top which collects the rainwater. The rainwater collected in the measuring cylinder gives the measure of rainfall.
3. Humidity
It is defined as ‘the amount of water vapor in the air which causes dampness of air’. Air has the ability to hold certain. amount of water vapor. The capacity of air to hold water increases with the rise in temperature and falls if heavy rainfall occurs. The humidity is measured by an instrument called a hygrometer which consists of two thermometers.
The bulb of one thermometer is wet and the other is dry.
4. Wind Speed
It is caused due to the difference in air pressure. During summer, the wind blows from the Indian ocean and the Bay of Bengal and causes rain in India while during winter, it blows from the mountain of north India towards the northern plain and causes cold weather (winter season).
Weather Prediction
The prediction of weather is done by scientists, called meteorologists, who study the changes in the weather. The weather is predicted by studying the patterns of weather and the factors affecting them. The science which deals with the study of weather is called meteorology. In India, the weather reports are prepared by the Meteorological Department of Government. This department collects data on temperature, wind, etc., and predicts whether on television or radio, or newspaper. The weather report is recorded every day in the form of graph and published in a table form showing readings of different elements of weather.
The difference in Time of Sunrise and Sunset
There is a difference in the time of sunrise during summer and winter. In summer the sun rises earlier in the morning and the sun sets late in the evening during the month of June, while the sun rises late and sets early in the month of December.
Therefore, days are longer and night shorter in summer while day is shorter and night is longer during winter.
Climate
‘The average weather pattern taken over a long time is called the climate of that place.’ Different places in the world have different types of climate. The annual record of long-term average temperature and rainfall at a particular place is called a climate chart. It gives an idea about the climate at a particular place during a specific period of the year. The major factor which determines the climate of a place is called latitude (imaginary lines on Earth).
Factors that Determine the Climate
The several factors that determine the climate at a place are
- Distance from the sea Climate of a place varies according to the closeness of the sea. The places that are near the sea, are moderate (not too hot nor too cold), e.g. Mumbai, Chennai. While the places that are away from the sea have extreme climates, having very hot summers or too cold winters, e.g. Delhi.
- Altitude or height above sea level Climate also varies according to the altitude. The higher altitudes are cooler, e.g. Himalayas.
- Humidity It also determines the climate of a place. Kolkata and Kerala have high humidity, while. Rajasthan and Haryana have low humidity.
Climates in India
The climate of India varies in different regions. These can be described below:
- The northern region of the Himalayas has a cold and moderately wet climate (e.g. Kashmir).
- Plains have a moderately hot and wet climate (e.g. Uttar Pradesh).
- South has a very hot and wet climate (e.g. Kerala).
- The western region has a hot and dry climate (e.g. Rajasthan).
- North-Eastern India has a wet climate (e.g. Assam) and receives rain for a major part of the year.
| Language English | English |
| No. of Pages | 12 |
| PDF Size | 1 MB |
| Category | Education |
| Source/Credits | – |
Related PDFs
Democracy And Education PDF By John Dewey In English
Bholi Class 10 Questions And Answers PDF
Class 10 Science Chapter 9 Heredity and Evolution Notes PDF
Silk Road Class 11 Questions And Answers PDF
Weather, Climate, And Adaptations Of Animals To Climate Class 7 Science Notes Chapter 7 PDF Free Download
