‘All Dimensional Formula List PDF English‘ PDF Quick download link is given at the bottom of this article. You can see the PDF demo, size of the PDF, page numbers, and direct download Free PDF of ‘All Dimensional Formula List English’ using the download button.
All Dimensional Formula List PDF Free Download
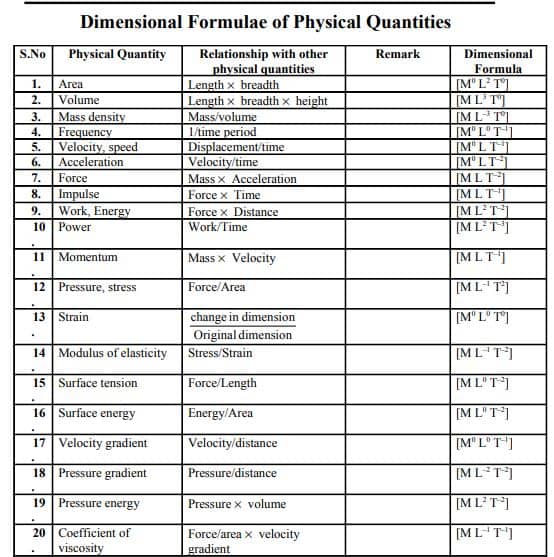
All-Dimensional Formula List With SI Unit
What do you mean by dimensions of physical quantity?
Each derived quantity requires proper power for fundamental quantities to represent it. The powers of fundamental quantities, through which they are to be raised to represent unit-derived quantity, are called dimensions. In other words, the dimensions of a physical quantity are the powers to which the base quantities (fundamental quantities) are raised to represent that quantity.
For example:
- The area is the product of two lengths.
Area = Length X breadth = [L] x [L] = [L2]
Therefore, [A] = [L2] That is, the dimension of the area is 2 dimensions in length and zero dimensions in mass and time.
Or [A] = [M0L2T0] - Similarly, the volume is the product of three lengths.
Volume = Length X breadth X height = [L] x [L] x [L] = [L3]
Therefore, [V] = [L3] That is, the dimension of volume is 3 dimensions in length and zero in mass and time.
Or [V] = [M0L3T0] - Similarly, acceleration is the rate of change of velocity per unit of time.
| Sl. No | Physical Quantity | Formula | Dimensional Formula | S.I Unit |
| 1 | Area (A) | Length x Breadth | [M0L2T0] | m2 |
| 2 | Volume (V) | Length x Breadth x Height | [M0L3T0] | m3 |
| 3 | Density (d) | Mass / Volume | [M1L-3T0] | gms-1 |
| 4 | Speed (s) | Distance / Time | [M0L1T-1] | ms-1 |
| 5 | Velocity (v) | Displacement / Time | [M0L1T-1] | ms-1 |
| 6 | Acceleration (a) | Change in velocity / Time | [M0L1T-2] | ms-2 |
| 7 | Acceleration due to gravity (g) | Change in velocity / Time | [M0L1T-2] | ms-2 |
| 8 | Specific gravity | Density of body/density of water at 4oC | No dimensions [M0L0T-0] | No units |
| 9 | Linear momentum (p) | Mass x Velocity | [M1L1T-1] | The universal constant of gravitation (G) |
| 10 | Force (F) | Mass x Acceleration | [M1L1T-2] | N |
| 11 | Work (W) | Force x Distance | [M1L2T-2] | J (Joule) |
| 12 | Energy (E) | Work | [M1L2T-2] | J |
| 13 | Impulse (I) | Force x Time | [M1L1T-1] | Ns |
| 14 | Pressure (P) | Force / Area | [M1L-1T-2] | Nm-2 |
| 15 | Power (P) | Work / Time | [M1L2T-3] | W |
| 16 | Energy/unit area | [M-1L3T-2] | Nm2kg-2 | |
| 17 | Moment of inertia (I) | Mass x (distance)2 | [M1L2T0] | kgm2 |
| 18 | Moment of force, moment of couple | Force x distance | [M1L2T-2] | Nm |
| 19 | Surface tension (T) | Force / Length | [M1L0T-2] | Nm-1 |
| 20 | Surface energy (E) | Stress/strain | [M1L0T-2] | Nm-1 |
| 21 | Force constant (x) | Force / Displacement | [M1L0T-2] | Nm-1 |
| 22 | Coefficient of viscosity ( η ) | [M1L-1T-1] | Nsm-2 | |
| 23 | Thrust (F) | Force | [M1L1T-2] | N |
| 24 | Tension (T) | Force | [M1L1T-2] | N |
| 25 | Stress | Force / Area | [M1L-1T-2] | Nm-2 |
| 26 | Strain | Change in dimension / Original dimension | No dimensions [M0L0T-0] | No unit |
| 27 | Modulus of Elasticity (E) | Length/length | [M1L-1T-2] | Nm-2 |
| 28 | Radius of gyration (k) | Distance | [M0L1T0] | m |
| 29 | Angle ( θ), Angular displacement | Arc length / Radius | No dimensions [M0L0T-0] | rad |
| 30 | Trigonometric ratio ( sin θ, cos θ, tan θ, etc) | Density of substance/density of water at 4oC | No dimensions [M0L0T-0 | No unit |
| 31 | Angular velocity( ω ) | Angle / Time | [M0L0T-1] | rad s-1 |
| 32 | Angular acceleration( α ) | Angular velocity / Time | [M0L0T-2] | rad s-2 |
| 33 | Angular momentum (J) | Moment of inertia x Angular velocity | [M1L2T-1] | kgm2s-1 |
| 34 | Torque (????) | Moment of inertia x Angular acceleration | [M1L2T-2] | Nm |
| 35 | Velocity gradient | Velocity / Distance | [M0L0T-1] | s-1 |
| 36 | Rate flow | Volume / Time | [M0L3T-1] | m3s-1 |
| 37 | Wavelength( ???? ) | Length of a wavelet | [M0L1T0] | m |
| 38 | Frequency( | Number of vibrations/second or 1/time period | [M0L0T-1] | Hz or s-1 |
| 39 | Angular frequency (ω) | 2π x frequency | [M0L0T-1] | |
| 40 | Planck’s constant (h) | Energy / Frequency | [M1L2T-1] | Js |
| 41 | Buoyant force | Force | [M1L1T-2] | N |
| 42 | Relative density | Pressure / Distance | No dimensions [M0L0T-0] | No unit |
| 43 | Pressure gradient | Energy/temperature | [M1L-2T-2] | Nm-3 |
| 44 | Pressure energy | Pressure x Volume | [M1L2T-2] | J |
| 45 | Temperature | —— | [M0L0T0K1] | K |
| 46 | Heat (Q) | Energy | [M1L2T-2] | J |
| 47 | Latent heat (L) | Heat / Mass | [M0L2T-2] | Jkg-1 |
| 48 | Specific heat (S) | [M0L2T-2K-1] | Jkg-1K-1 | |
| 49 | Thermal expansion coefficient or thermal expansivity | [M0L0T0K-1] | K-1 | |
| 50 | Thermal conductivity | [M1L1T-3K-1] | Wm-1K-1 | |
| 51 | Bulk modulus or (compressibility)-1 | [M1L-1T-2] | Nm-2 or Pascals | |
| 52 | Centripetal acceleration | [M0L1T-2] | ||
| 53 | Stefan constant (σ) | [M1L0T-3K-4] | Wm−2K−4 | |
| 54 | Wien constant | Wavelength X temperature | [M0L1T0K1] | mK |
| 55 | Gas constant (R) | [M1L2T-2K-1] | JK-1 | |
| 56 | Boltzmann constant (K) | Potential difference/distance | [M1L2T-2K-1] | JK-1 |
| 57 | Charge (q) | Current x time | [M0L0T1A1] | C |
| 58 | Current density | Current / area | [M0L-2T0A1] | A m−2 |
| 59 | Electric potential (V), voltage, electromotive force | Work / Charge | [M1L2T–3A-1] | V |
| 60 | Resistance (R) | Potential difference / Current | [M1L2T–3A-2] | ohms (Ω) |
| 61 | Capacitance | Charge / potential difference | [M–1L–2T4A2] | F (Farad) |
| 62 | Electrical resistivity or (electrical conductivity)-1 | [M1L3T-3A–2] | Ωm ( resistivity) | |
| 63 | Electric field (E) | Force / Charge | [M1L1T-3A-1] | NC-1 |
| 64 | Electric flux | Electric field X area | [M1L3T–3A-1] | Nm2C-1 |
| 65 | Electric dipole moment | Torque / electric field | [M0L1T1A1] | C m |
| 66 | Electric field strength or electric intensity | Magnetic flux/current | [M1L1T-3A-1] | NC-1 |
| 67 | Magnetic field (B), magnetic flux density, magnetic induction | [M1L0T-2A-1] | T (Tesla) | |
| 68 | Magnetic flux (Φ) | Magnetic field X area | [M1L2T-2A-1] | Wb (Weber) |
| 69 | Inductance | Magnetic field strength (H), magnetic intensity, or magnetic moment density | [M1L2T-2A-2] | H (Henry) |
| 70 | Magnetic dipole moment | Torque /field or current X area | [M0L2T0A1] | Am2 |
| 71 | Magnetic moment/volume | Recession speed/distance | [M0L-1T0A1] | Am-1 |
| 72 | Hubble constant | Intensity of wave/speed of light | [M0L0T-1] | s-1 |
| 73 | Intensity of wave | (Energy/time)/area | [M1L0T-3] | Wm-2 |
| 74 | Radiation pressure | Energy/volume | [M1L–1T-2] | |
| 75 | Energy density | Permittivity constant (of free space) | [M1L-1T-2] | Jm-3 |
| 76 | Critical velocity | [M0L1T-1] | ms-1 | |
| 77 | Escape velocity | [M0L1T-1] | ms-1 | |
| 78 | Heat energy, internal energy | Work ( = Force X distance) | [M1L2T-2] | J |
| 79 | Kinetic energy | [M1L2T-2] | J | |
| 80 | Potential energy | Mass X acceleration due to gravity X height | [M1L2T-2] | J |
| 81 | Rotational kinetic energy | [M1L2T-2] | J | |
| 82 | Efficiency | No dimensions [M0L0T0] | No unit | |
| 83 | Angular impulse | Torque X time | [M1L2T-1] | Js (Joule second) |
| 84 | The energy emitted / time | [M-1L-3T4A2] | F m-1 | |
| 85 | Permeability constant (of free space) | [M1L1T-2A-2] | NA-2 | |
| 86 | Refractive index | No dimensions [M0L0T0] | No unit | |
| 87 | Faraday constant (F) | Avogadro constant X elementary charge | [M0L0T1A1 mol-1] | C mol-1 |
| 88 | Wave number | [M0L-1T0] | ||
| 89 | Radiant flux, Radiant power | Binding energy of the nucleus | [M1L2T-3] | W(Watt) |
| 90 | Luminosity of radiant flux or radiant intensity | [M1L2T-3] | W sr-1 (Watt/steradian) | |
| 91 | Luminous power or luminous flux of source | [M1L2T-3] | lm (lumen) | |
| 92 | Luminous intensity or illuminating power of source | Luminous flux / Solid angle | [M1L2T-3] | cd (candela) |
| 93 | Intensity of illumination or luminance (Lv) | [M1L0T-3] | cd m-2 | |
| 94 | Relative luminosity | Luminous flux of a source of given wavelength / luminous flux of peak sensitivity wavelength(555 nm) source of the same power | No dimensions [M0L0T0] | No unit |
| 95 | Luminous efficiency | Total luminous flux / Total radiant flux | No dimensions [M0L0T0] | No unit |
| 96 | Illuminance or illumination | Luminous flux incident / Area | [M1L0T-3] | lx (lux) |
| 97 | Mass defect | (Sum of masses of nucleons) – (mass of the nucleus) | [M1L0T0] | |
| 98 | Binding energy of nucleus | [M1L2T-2] | ||
| 99 | Decay constant | 0.693 / half-life | [M0L0T-1] | |
| 100 | Resonant frequency | [M0L0T-1A0] | ||
| 101 | Quality factor or Q-factor of coil | No dimensions [M0L0T0] | No unit | |
| 102 | Power of lens | [M0L-1T0] | D (dioptre) | |
| 103 | Magnification | Image distance / Object distance | No dimensions [M0L0T0] | No unit |
| 104 | Fluid flow rate | [M0L3T-1] | m3s-1 | |
| 105 | Capacitive reactance (Xc) | (Angular frequency X capacitance)-1 | [M1L2T-3A-2] | ohms (Ω) |
| 106 | Inductive reactance (XL) | (Angular frequency X inductance) | [M1L2T-3A-2] | ohms (Ω) |
| Author | – |
| Language | English |
| No. of Pages | 5 |
| PDF Size | 0.1 MB |
| Category | Education |
All Dimensional Formula List PDF Free Download

It is very good website 🥰🥰😍😍
Thank you