‘UP Board Class 12 Biology Practical Book’ PDF Quick download link is given at the bottom of this article. You can see the PDF demo, size of the PDF, page numbers, and direct download Free PDF of ’12th Biology Practical Book Answers’ using the download button.
UP Board class 12 Prayogik Jeev Vigyan (Biology Lab Manual) PDF Free Download
Class 12 Biology practical questions with answers Book For up Board
EXPERIMENT-1
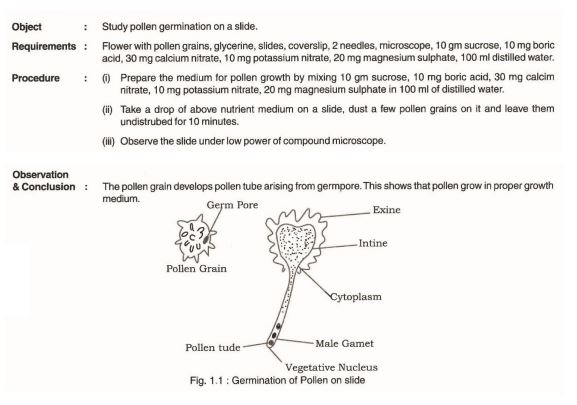
Object: Study pollen germination on a slide.
Requirements: Flower with pollen grains, glycerine, slides, coverslip, 2 needles, microscope, 10 gm sucrose, 10 mg boric acid, 30 mg calcium nitrate, 10 mg potassium nitrate, 20 mg magnesium sulfate, 100 ml distilled water. 21
Procedure
(1) Prepare the medium for pollen growth by mixing 10 gm sucrose, 10 mg boric acid, 30 mg calcium nitrate, 10 mg potassium nitrate, and 20 mg magnesium sulfate in 100 ml of distilled water.
(2) Take a drop of the above nutrient medium on a slide, dust a few pollen grains on it, and leave them undisturbed for 10 minutes
(3) Observe the slide under the low power of the compound microscope.
The pollen grain develops a pollen tube arising from the empire. This shows that pollen grow in proper growth
EXPERIMENT-2
Object: Isolation of DNA from available plant material such as spinach, green pea seeds, papaya, etc.
Materials :
Spinach leaves/Pea seeds/Papaya, Sand test tube, 50 ml beakers, Cheesecloth, Mortar and pestle,
Required : 10ml graduated cylinder
Procedure :
- Choose 2-3 spinach leaves. Remove any stems if present.
- Place 1 ml of distilled water in a mortar and pestle along with leaves. Add a small pinch of sand and grind until spinach looks like creamed spinach. Add the contents of the mortar and pestle to a 50 ml beaker.
- Add 1 ml of 50% detergent solution and 9 ml salt solution to spinach. Mix well with a glass stir rod. 4. Place on a hot plate and heat until boiling. Remove from heat and let sit for 2 minutes.
- Put on ice for 5 minutes so that it cools down.
- Pour spinach mature (supernatant) through cheesecloth into a clean beaker. 7. Pour the supernatant into a test tube then add 1 ml of freshly prepared contact lens cleaning solution.
- Carefully layer 6 mi chilled 95% ethanol solution onto the green supernatant using a 10 ml graduated cylinder.
- Slowly pour ethanol down the side of the test tube.
- Try not to let the two layers mix together.
- Using the wire loop, spool the DNA by gently swirling the loop at the interface between the green supernatant and the clear ethanol. The DNA will congeal at the point where the two layers meet.
Object :
Flowers adapted to pollination by different agencies(wind, insect) Requirements: Sunflower (for insect posination), Wheat flower (for wind pollination), Bottle-Brush (for bird pollination). forceps, slide, dissecting microscope and needs.
Procedure :
For insect pollination
(1) Tako a sunflower. Observe the central black disc florets and peripheral yellow ray floret flowers
(2) Disk forets are sessile, bisexual, tubular, eplaynous flowers born on receptacle Sepals are modified intro hair.
Petals are fused Stamens are five with fund anthers and free Staments (syngensis)
(R) Ray florets are yellow, unisexual and pistillate or neuter, sopels like ray floret, petals five, fused, ovate, stamens absent. Pistil has bifid stigma, style long, ovary, round shaped. Pollination:
The disc florets are bisexual and protandrous (stamens mature before pistil). So cross pollination occurs
This pollination is mainly brought by insects. Mechanism:
(i) Anthers mature first and release pollen grains. At this time stigma is immature and remain hidden in compressed form, below anthers.
(ii)The insects like honey bees walk over the disk florets to suck nectar from the base of style. Thepollen grains stick to their legs and abdomen.
(iii)When these insects visit flowers of another plant of same species, they shed the pollen grain over stigma and bring about cross pollination.
(v) As stigma reaches maturity the style elongates and the stigma comes above anthers, exposed in environment. Insect may pollinate it while collecting nectar.
(v)It cross pollination fails, then the stigma curls down towards anthers to pick up pollen grains and bring about sell pollination.
(vi) Visit you school garden and observe pollination process.
| Author | – |
| Language | English |
| No. of Pages | 25 |
| PDF Size | 7.1 MB |
| Category | Education |
| Source/Credits | Google.Drive.Com |
UP Board class 12 Prayogik Jeev Vigyan (Biology Lab Manual) PDF Free Download
