‘Linked List In Data Structure’ PDF Quick download link is given at the bottom of this article. You can see the PDF demo, size of the PDF, page numbers, and direct download Free PDF of ‘Linked List In Data Structure’ using the download button.
Linked List In Data Structure PDF Free Download
Linked List In Data Structure
If arrays accommodate similar types of data types, linked lists consist of elements with different data types that are also arranged sequentially.
But how are these linked lists created?
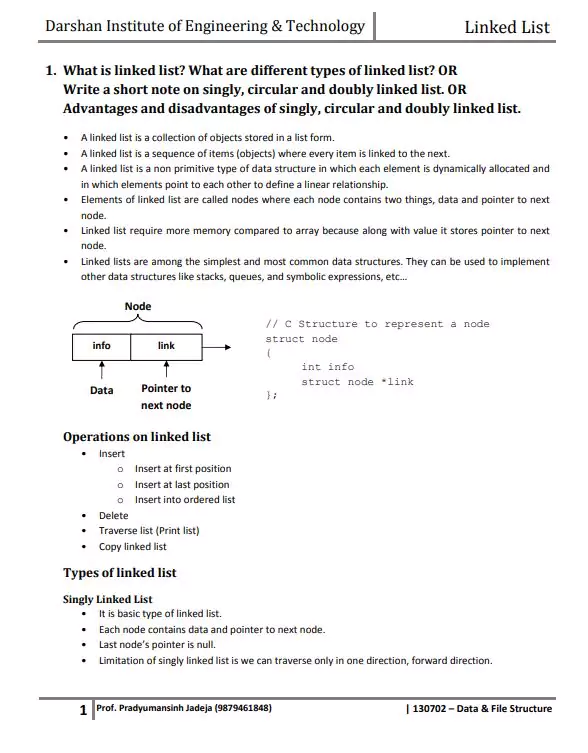
A linked list is a collection of “nodes” connected together via links.
These nodes consist of the data to be stored and a pointer to the address of the next node within the linked list.
In the case of arrays, the size is limited to the definition, but in linked lists, there is no defined size. Any amount of data can be stored in it and can be deleted from it.
There are three types of linked lists −
- Singly Linked List − The nodes only point to the address of the next node in the list.
- Doubly Linked List − The nodes point to the addresses of both the previous and next nodes.
- Circular Linked List − The last node in the list will point to the first node in the list. It can either be singly linked or doubly linked.
Linked List Representation
Linked list can be visualized as a chain of nodes, where every node points to the next node.
As per the above illustration, the following are the important points to be considered.
- Linked List contains a link element called first (head).
- Each link carries a data field(s) and a link field called next.
- Each link is linked with its next link using its next link.
- Last link carries a link as null to mark the end of the list.
Types of Linked Lists
Following are the various types of linked list.
Singly Linked Lists
Singly-linked lists contain two “buckets” in one node; one bucket holds the data and the other bucket holds the address of the next node of the list.
Traversals can be done in one direction only as there is only a single link between two nodes of the same list.
Doubly Linked Lists
Doubly Linked Lists contain three “buckets” in one node; one bucket holds the data and the other buckets hold the addresses of the previous and next nodes in the list.
The list is traversed twice as the nodes in the list are connected to each other from both sides.
Circular Linked Lists
Circularly linked lists can exist in both singly linked lists and doubly linked lists.
Since the last node and the first node of the circular linked list are connected, the traversal in this linked list will go on forever until it is broken.
Basic Operations in the Linked Lists
The basic operations in the linked lists are insertion, deletion, searching, display, and deleting an element at a given key. These operations are performed on Singly Linked Lists as given below −
- Insertion − Adds an element at the beginning of the list.
- Deletion − Deletes an element at the beginning of the list.
- Display − Displays the complete list.
- Search − Searches an element using the given key.
- Delete − Deletes an element using the given key.
Insertion Operation
Adding a new node in the linked list is a more than one-step activity. We shall learn this with diagrams here. First, create a node using the same structure and find the location where it has to be inserted.
| Language | English |
| No. of Pages | 26 |
| PDF Size | 1 MB |
| Category | Education |
| Source/Credits | – |
Related PDFs
Rajiv Swagruha Bandlaguda Allotment List PDF
Linked List In Data Structure PDF Free Download
